1 Identify any hazards that must be prevented, eliminated or reduced
2 Identify the critical control points (CCPs) at the steps at which control is essential
3 Establish critical limits at CCPs
4 Establish procedures to monitor the CCPs
5 Establish corrective actions to be taken if a CCP is not under control
6 Establish procedures to verify whether the above procedures are working effectively
7 Establish documents and records to demonstrate the effective application of the above measures
The HACCP approach provides a systematic way of identifying food safety hazards and making sure that they are being controlled day-in, day-out. This involves the following four steps: Plan, Do, Check Act.
Plan what needs to be done to maintain food safety and write it down.
Do what you plan to do to maintain food safety.
Check that you are doing what you planned to do to maintain food safety and write down what was checked and when.
Act to correct any food safety problems and write down what has been done about the problem and review to ensure the plan is effective.
There are many laws governing the safe production and sale of food. The minimum standard requires all food businesses to be kept clean and disinfected, the structure and layout of the premises must be so to protect food from risks of contamination and all food handlers must be supervised and trained as appropriate.
Article 5 of Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 requires every food business to put in place, implement and maintain a permanent and documented food safety management system based on HACCP principles.
The level of documentation and associated record-keeping will depend on the nature and size of the food business. As the Information specific businesses follow depends on the business size and type of food business they are, there are flexibility and differences in what needs to be kept.
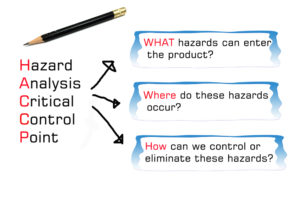
In its simplest form, HACCP is an assessment of all the chemical, physical and biological hazards that may contaminate our food (from farm to fork) and cause illness or injury when consumed. When these hazards are identified, appropriate steps must then be taken to eliminate the hazard where possible or reduce the risk (illness or injury) to a safe and acceptable level. The law also requires certain records to be kept as proof that food safety is being managed.

