When a person suffers a cut, the first thing that happens is that the blood vessels at the site of the injury constrict. This helps to slow the flow of blood and prevent excessive bleeding. At the same time, the body begins to release certain chemicals that help to promote the formation of a blood clot.
One of these chemicals is called platelets. Platelets are small, disk-shaped cells that are found in the blood. When a person suffers a cut, the platelets begin to stick to the injured blood vessels and to each other. This forms a kind of plug or barrier that helps to stop the bleeding.
Another chemical that is involved in blood clotting is called fibrin. Fibrin is a protein that is produced by the body when a person suffers a cut. It helps to strengthen the platelet plug and create a stronger barrier to stop the bleeding.
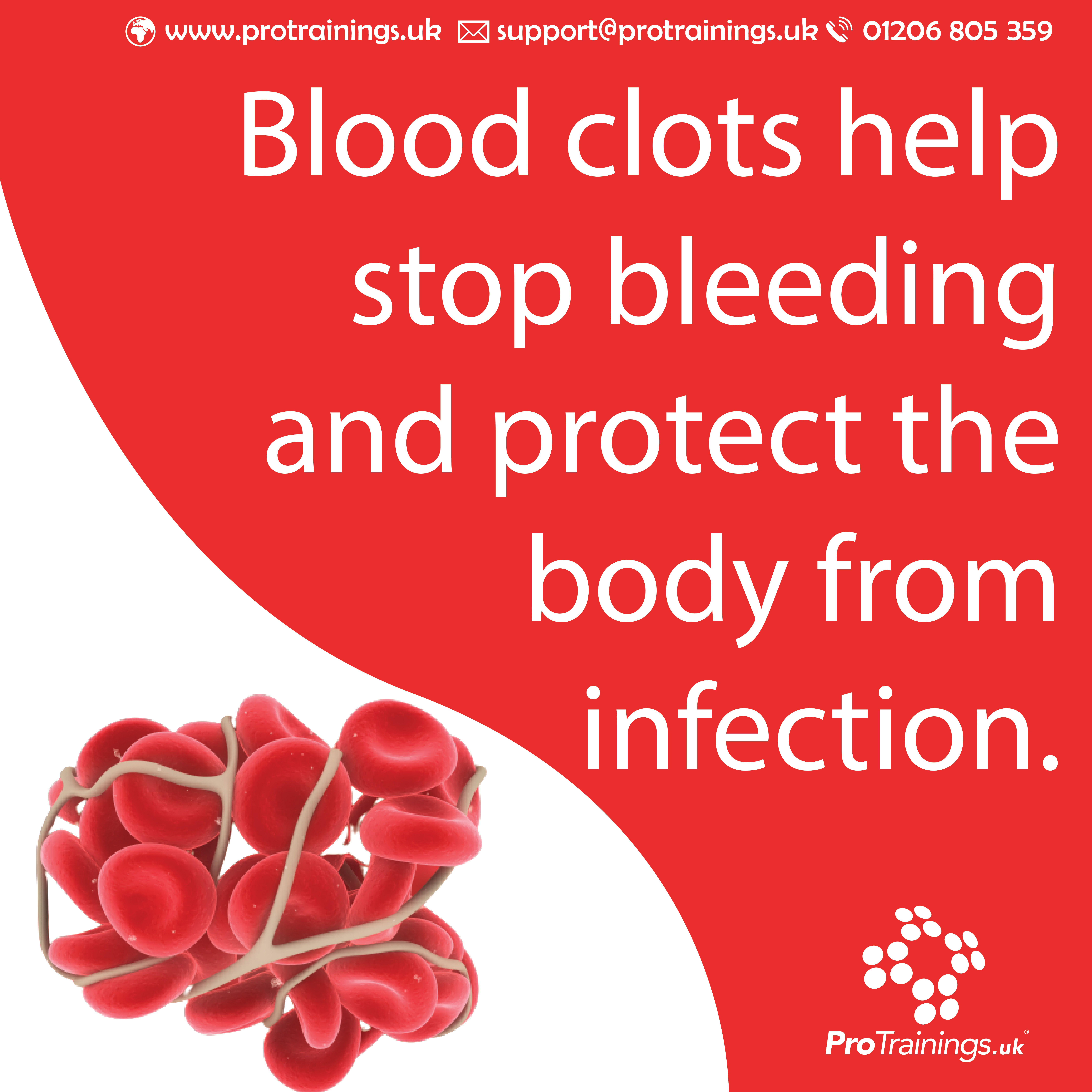
As the blood continues to flow, the platelets and fibrin work together to form a mesh-like structure that helps to hold the blood in place and prevent it from flowing out of the body. This mesh-like structure is what we know as a blood clot.
Once the blood clot has formed, the body begins to repair the injured blood vessels. This process is called healing. As the blood vessels heal, the blood clot is gradually broken down and absorbed back into the body.
The formation of blood clots is a crucial part of the body’s natural healing process. However, it is important to note that blood clots can sometimes cause problems. In some cases, blood clots can break loose and travel to other parts of the body, where they can become lodged in the blood vessels and block the flow of blood. This can lead to serious health complications, such as heart attack or stroke.
It is also important to seek medical attention if you suffer a cut that does not stop bleeding after a few minutes. This could be a sign that there is something preventing the blood from clotting properly, such as a deficiency in one of the chemicals involved in the clotting process. In such cases, it may be necessary for a doctor to give the person medication to help the blood clot.
In conclusion, blood clots are an important part of the body’s natural response to injury. They help to stop the bleeding and protect the body from infection. While blood clots can sometimes cause problems, they are generally a crucial part of the healing process. If you are concerned about blood clots or are experiencing problems with bleeding, it is important to speak with a doctor.
Learn more about first aid training, whether on our video online platform, blended or a face to face course locally or at your workplace cal ProTrainings on 01206 805359 or email support@protrainings.uk or visit www.protrainings.uk/courses. To buy first aid kits or equipment, visit www.first-aid-online.co.uk
